Overall procedure¶
This program performs simulation as follows (See Fig. 4 ):
Read a input file for the numerical condition.
(Optional) Read input files for the Hamiltonian and the right hand side vector.
(Optional) Read a file for the restart (\(\alpha\), \(\beta\), residual vectors)
(Bi)CG iteration with \(K\omega\) library
Output results (Green’s function, residual vectors, \(\alpha\), \(\beta\))
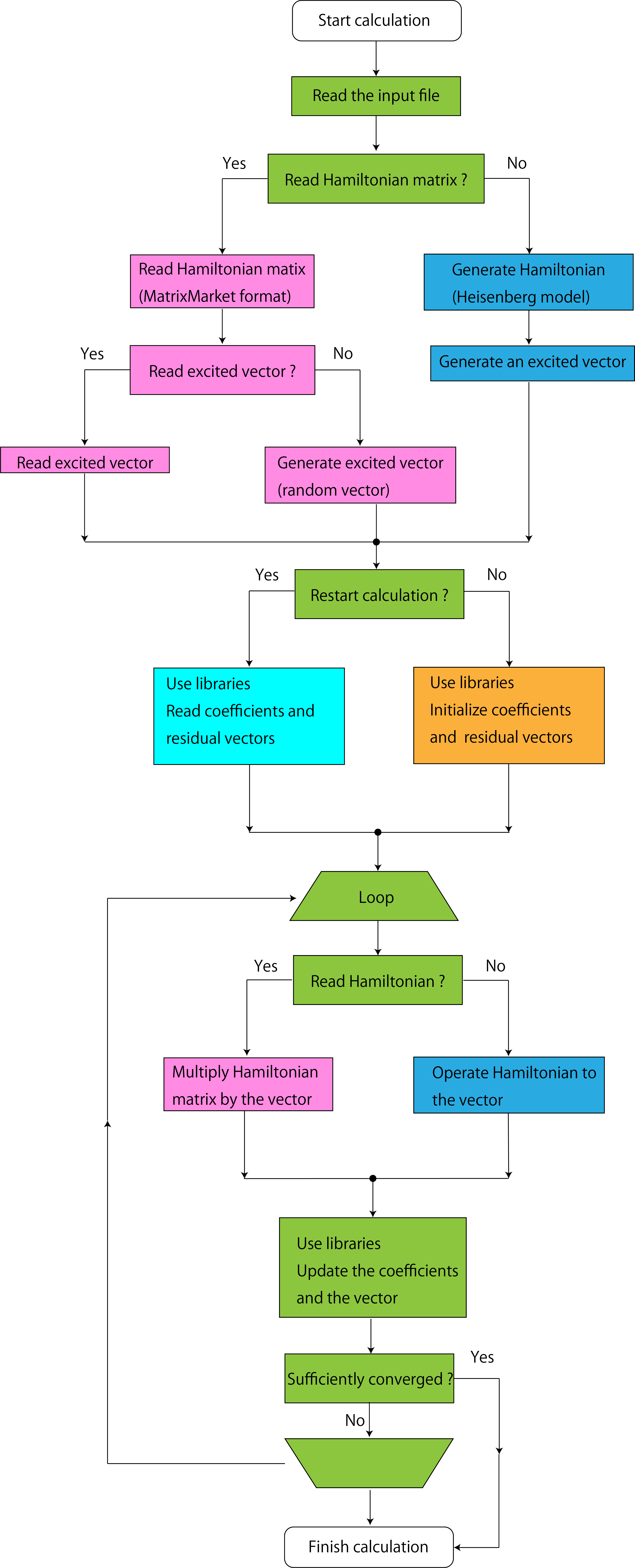
Figure 4: Schematic flow of the calculation of this program.¶
We introduce the detailed procedure as follows. The format of each file is written in Format of files.
Calculation from scratch¶
Prepare input file¶
In this input file, we specify the frequency grid, the maximum number of iteration, etc.
A example of this input file is shown as follow.
&filename
inham = ""
invec = ""
/
&ham
nsite = 4
Jx = 1d0
Jy = 1d0
Jz = 1d0
Dz = 0d0
/
&cg
maxloops = 100
convfactor = 6
/
&dyn
calctype = "normal"
nomega = 100
omegamin = (-2d0, 0.1d0)
omegamax = ( 1d0, 0.1d0)
outrestart = .TRUE.
/
where InHam is the file-name for the Hamiltonian in the MatrixMarket format,
InVec is the file-name of the right hand side vector,
NOmega is the number of frequencies where the dynamical Green’s function
is computed.
OmegaMin is the lower limit of the frequency \(z\),
OmegaMax is the upper limit of the frequency \(z\).
These complex frequencies must be written as “({Real part}, {Imaginaly part})”.
The frequency grid is defined as
MaxLoops is the maximum number of iterations.
For the details of this input file, see “Namelist” file.
The string variable must be specified with two ' or ".
(Optional) Prepare input file for the Hamiltonian and RHS vector¶
Prepare input files for the Hamiltonian (MatrixMarket format) and right hand side vector.
An example of the file of the right hand side vector is shown as follows:
256
0.01 0.0
0.05 0.0
0.1 0.0
(continue ...)
Details of the file format is written in “InHam” file and “InVec” file.
Launch¶
Execute a program ShiftK.out with a namelist file namelist.def
as follows:
$ ShiftK.out namelist.def
Output¶
The following files are generated in output/ directory (this directory is
also generated by this program).
TriDiagComp.dat, ResVec.dat, dynamicalG.dat
where
TriDiagComp.dat contains the parameters for the restart,
ResVec.dat contains the residual vector,
dynamicalG.dat contains the dynamical Green’s function.
The format of these file is written in
Residual vector - Dynamical Green’s function.
Catch up¶
Compute the Green’s function at the different frequency by using the information
of output/TriDiagComp.dat that are generated in the previous run.
This calculation does not require the matrix-vector product.
Modify the namelist file¶
Change calctype parameter in the file namelist.def
from "normal" to "recalc".
OmegaMin, OmegaMax, etc. can be modified.
Launch¶
Execute a program ShiftK.out with a namelist file namelist.def
as follows:
$ ShiftK.out namelist.def
The output/dynamicalG.dat will be overwritten.
Output¶
The same output files as the previous section are generated.
Restart¶
Compute the Green’s function at the different frequency by using the information
of output/TriDiagComp.dat and output/ResVec.dat
that are generated in the previous run.
Modify the namelist file¶
Change calctype parameter in the file namelist.def
from "normal" to "restart".
OmegaMin, OmegaMax, etc. can be modified.
Parameters InHam , InVec, and the files of the Hamiltonian
and RHS vector can not be modified.
Launch¶
Execute a program ShiftK.out with a namelist file namelist.def
as follows:
$ ShiftK.out namelist.def
The output/dynamicalG.dat will be overwritten.
Output¶
The following files are generated (or are overwritten) in output/ directory.
TriDiagComp.dat, ResVec.dat, dynamicalG.dat
where
TriDiagComp.dat contains the parameters for the restart,
ResVec.dat contains the residual vector,
dynamicalG.dat contains the dynamical Green’s function.
The format of these file is written in
Residual vector - Dynamical Green’s function.
