Format of files¶
Input files¶
“Namelist” file¶
This file has four namelist (filename, ham, cg, dyn).
For the details of the namelist of fortran, see some books and Web page for fortran.
&filename
inham = ""
invec = ""
/
&ham
nsite = 4
Jx = 1d0
Jy = 1d0
Jz = 1d0
Dz = 0d0
/
&cg
maxloops = 100
convfactor = 6
/
&dyn
calctype = "normal"
nomega = 100
omegamin = (-2d0, 0.1d0)
omegamax = ( 1d0, 0.1d0)
outrestart = .TRUE.
/
In the namelist “filename”`, we specify the file names of the Hamiltonian and the RHS vector.
InHamType : string (default:
"")Description : The name of the file for the Hamiltonian in the MatrixMarket format (full path or relative path). If this parameter is not specified, the Hamiltonian of the 1D spin chain is generated with the parameters in
hamnamelist.InVecType : string (default:
"")Description : The name of the file for the right hand side vector. If this parameter is not specified, the RHS vector is generated as follows: First the ground-state vector is computed. Then RHS vector is calculated by operating \({\hat S}_{1 z}\) (\(z\) component of the spin at site 1) to the ground-state vector. Therefore, we assume the computed system is the one-dimensional spin chain.
"ham"namelist is read only whenInHamis not specified. The parameters in this namelist are used to generate the Hamiltonian of the one-dimensional spin chain (See Fig. 2)
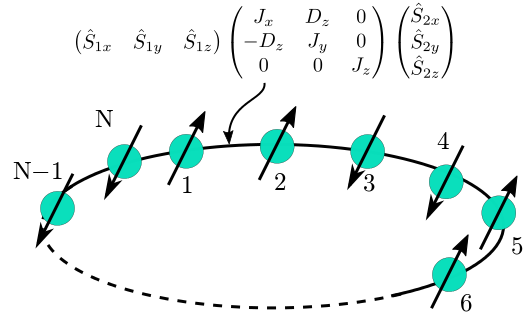
Figure 2: Schematic picture of the one-dimensional spin chain.¶
nsiteType : int (default:
4)Description : The number of sites in the 1D spin chain model.
JxType : double (default:
1.0)Description : \(J_x\) for the Heisenberg model.
JyType : double (default:
1.0)Description : \(J_y\) for the Heisenberg model.
JzType : double (default:
1.0)Description : \(J_z\) for the Heisenberg model.
DzType : double (default:
0.0)Description : The parameter of the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (\(D_z\)).
cg namelist has parameters
for specifying the numerical condition for the
(Bi)Conjugate-gradient method.
MaxLoopsType : int (default: the dimension of the Hamiltonian)
Description : The maximum number of iterations.
ConvfactorType : int (default:
8)Description : Convergence threshold. If the 2-norm of the residual vector becomes smaller than \(10^{-{\tt Convfactor}}\), the calculation finishes.
dyn has the parameters for the computation of the spectrum.
OmegaMinType : Complex (default: If
invecis not specified, the real part of it becomes the smallest eigenvalue, and the imaginary part of it becomes \(\times0.01\) times the difference between the largest- and the smallest- eigenvalue. Ifinvecis specified, the default value becomes(0.0, 0.01))Description : The smallest frequency.
OmegaMaxType : Complex (default: If
invecis not specified, the real part of it becomes the largest eigenvalue, and the imaginary part of it becomes \(\times0.01\) times the difference between the largest- and the smallest- eigenvalue. Ifinvecis specified, the default value becomes(1.0, 0.01))Description : The largest frequency.
NOmegaType : int (default:
10)Description : The number of frequencies.
outrestartType : Logical (default:
.FALSE.)Description : Whether data for restart will be written (
.TRUE.) or not (.FALSE.).calctypeType : String. Choose from
"normal","recalc","restart". (default:"normal")Description :
"normal"for computing with the Krylov subspace from scratch."recalc"for computing with the Krylov subspace generated in the previous calculation. In this case, the matrix-vector product is not performed. The convergence is not guaranteed."restart"for restarting the calculation from the previous run. In this case, the calculation continues until the convergence is achieved or the number of iteration becomesMaxLoops.
“InHam” file¶
The Hamiltonian is written in the MatrixMarket format.
Example of the “InHam” file:
%%MatrixMarket matrix coordinate complex hermitian
16 16 20
1 1 1.000000 0.000000
3 2 0.500000 0.000000
5 3 0.500000 0.000000
6 4 0.500000 0.000000
6 6 -1.000000 0.000000
7 6 0.500000 0.000000
9 2 0.500000 0.000000
9 5 0.500000 0.000000
10 6 0.500000 0.000000
11 4 0.500000 0.000000
11 7 0.500000 0.000000
11 10 0.500000 0.000000
11 11 -1.000000 0.000000
12 8 0.500000 0.000000
13 6 0.500000 0.000000
13 11 0.500000 0.000000
14 12 0.500000 0.000000
15 8 0.500000 0.000000
15 14 0.500000 0.000000
16 16 1.000000 0.000000
- First row:
Arbitrary string (such as comment).
- Second row:
The number of rows, columns, and non-zero elements (in the lower triangle part).
- Third row - End:
The row- and the column- index, and the real- and imaginary- part of the non-zero element (in the lower triangle part).
“InVec” file¶
Right hand side vector is contained.
Example of the “InVec” file:
8192
0.02 0.01
0.02 0.001
(continue...)
First row: [ int01 ]
Type : int
Description : The dimension of the Hilbert space. It must be the same as the dimension of the Hamiltonian.
Second row - End: [ double01 ] [ double02 ]
Type : double
Description : The element of the RHS vector. [ double01 ] is the real part, and [ double02 ] is the imaginary part.
Coefficients for restart¶
The coefficient \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) are contained.
The name of the generated file is TriDiagComp.dat.
The example of this file:
1000
1.0 0.0
0.1 0 0.01 0
0.2 0 0.021 0
(continue...)
2.1 -0.5
3.1 4.0
(continue...)
First row: [ int01 ]
Type : int
Description : The length of \(\alpha, \beta\). It is the same as the number of iterations in the previous run.
Second row: [ double01 ] [ double02 ]
Type : double
Description : The seed frequency \(z_{\rm seed}\). [ double01 ] is the real part of \(z_{\rm seed}\), and [ double02 ] is the imaginary par of \(z_{\rm seed}\).
Third row - 2 + [ int01 ]th row: [ double03 ] [ double04 ] [ double05 ] [ double06 ]
Type : double
Description : \(\alpha, \beta\) at the each iteration. [ double03 ] is the real part of \(\alpha\), [ double04 ] is the imaginary part of \(\alpha\), [ double05 ] is the real part of \(\beta\), [ double06 ] is the imaginary part of \(\beta\).
3 + [ int01 ]th row - 2 + \(2\times[\) int01 ]th row: [ double07 ] [ double08 ]
Type : double
Description : The product of the RHS vector and the residual vector at the each iteration. [ double07 ] is the real part of it, and [ double08 ] is the imaginary part of it.
Residual vector¶
The residual vector is contained for the restart.
The file name is ResVec.dat.
Example of this file:
8192
0.02 0.01
0.02 0.001
(continue...)
0.02 0.01
0.02 0.001
(continue... Only for BiCG)
First row: [ int01 ]
Type : int
Description : The dimension of the Hilbert space.
Second row - 1 + [ int01 ]th row: [ double01 ] [ double02 ]
Type : double
Description : Each element of the residual vector. [ double01 ] is the real part of it, and [ double02 ] is the imaginary part of it.
Third row - 1 + 2 \(\times\) [ int01 ]th row: [ double03 ] [ double04 ]
Type : double
Description : (Only when the Hamiltonian is a complex matrix) Each element of the shadow residual vector. [ double03 ] is the real part of it, [ double04 ] is the imaginary part of it.
Output file¶
Coefficient for restart¶
The format is the same as Coefficients for restart.
Residual vector¶
The format is the same as Residual vector.
Dynamical Green’s function¶
The dynamical Green’s function is contained.
Example of this file:
-10 0.001 0.001 -0.0001
-9.8 0.001 0.0012 -0.0002
-9.6 0.001 0.0014 -0.0003
(continue...)
First row - END: [ double01 ] [ double02 ] [ double03 ] [ double04 ]
[ double01 ], [ double02 ]
Type : double
Description : The real- ([ double01 ]) and the imaginary- ([ double02 ]) part of the frequency.
[ double03 ], [ double04 ]
Type : double
Description : The dynamical Green’s function. [ double01 ] is the real part of it, and [ double02 ] is the imaginary part of it.
