4.4. Number density of the hardcore Bosons on a square lattice¶
In this tutorial, we will calculate the chemical potential dependence of the number density of the hardcore Bose-Hubbard model with the nearest neighbor repulsive on a \(8\times8\) square lattice.
The following Python script (sample/dla/03_bosesquare/exec.py) performs DSQSS/DLA work-flow for each parameter (chemical potential) automatically.
import sys
import os.path
import subprocess
bindir = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv) > 1 else ''
name = 'amzu'
mus = [-4.0, -2.0, 0.0, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 6.0, 9.0, 9.5, 10.0, 12.0, 14.0]
output = open('{}.dat'.format(name), 'w')
for i,mu in enumerate(mus):
with open('std_{}.in'.format(i), 'w') as f:
f.write('''
solver = DLA
model_type = boson
M = 1
J = 1
U = 0
V = 3
beta = 10.0
lattice_type = square
D = 2
L = 8,8
nset = 4
ntherm = 100
ndecor = 100
nmcs = 100
''')
f.write('F = {}\n'.format(mu/4))
f.write('algfile = algorithm_{}.xml\n'.format(i))
f.write('outfile = res_{}.dat\n'.format(i))
cmd = [os.path.join(bindir, 'dsqss_pre.py'),
'-p', 'param_{}.in'.format(i),
'-i', 'std_{}.in'.format(i)]
subprocess.call(cmd)
cmd = [os.path.join(bindir, 'dla_B'), 'param_{}.in'.format(i)]
subprocess.call(cmd)
with open('res_{}.dat'.format(i)) as f:
for line in f:
if not line.startswith('R'):
continue
words = line.split()
if words[1] == name:
output.write('{} {} {}\n'.format(mu, words[3], words[4]))
This script receives the binary directory as an argument (if an environment variable $DSQSS_ROOT is set correctly, the argument can be omitted).
$ python exec.py $DSQSS_ROOT/bin
The result is written to amzu.dat (Fig. 4.2).
You can see a density plateau around \(\mu=6\) . In this region, a checker board solid phase due to repulsive interaction appears.
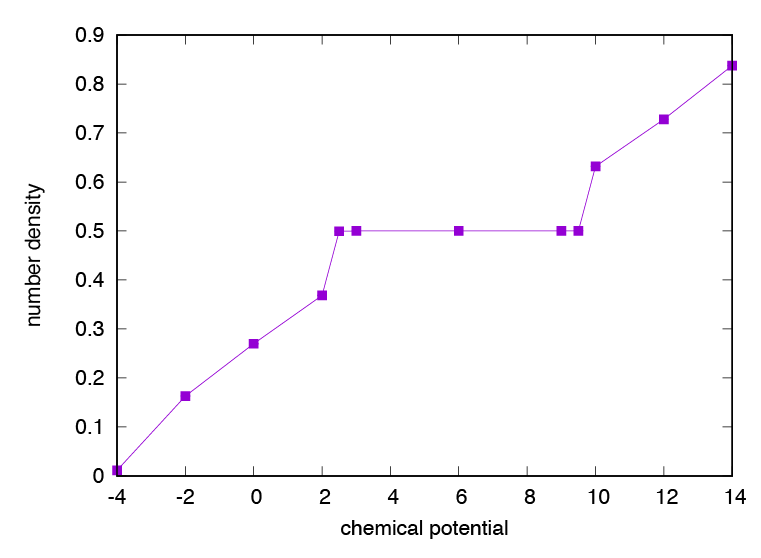
Fig. 4.2 Chemical potential dependence of number density of repulsive hardcore bosons.
